|
45 | 45 | - Wireshark: Open source sniffer. |
46 | 46 | - INetSim: Simulates commin Internet services. |
47 | 47 |
|
| 48 | +## Chapter 4 - Crash course in x86 disassembly |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +- C code => *compiler* => CPU Machine Code => *Disassembler* => Assembly Code |
| 51 | +- **Levels of Abstraction:** |
| 52 | + - **Hardware:** Electrical circuits that implements logical operations like XOR, AND, OR and NOT gates |
| 53 | + - **Microcode (firmware):** An interface between hardware and machine code |
| 54 | + - **Machine code:** List of Opcodes that tell the processor what to do |
| 55 | + - **Low-level languages:** Human readable version of a computer architeture's instruction set (assembly). |
| 56 | + - **High-level languages:** Programming languages like C, C++, ... Compiled to machine code. |
| 57 | + - **Interpreted languages:** Programming languages like Python, C#, java, ... Translated to bytecode that will be executed by a interpreter. |
| 58 | +- **Microprocessors Architectures:** x86, x64, SPARC, PowerPC, MIPS, ARM, etc. |
| 59 | +- **Von Neumann Architecture:** |
| 60 | + - **Central Processing Unit (CPU):** Executes code |
| 61 | + - **Control Unit:** Get instructions to execute from RAM using the Instruction Pointer register |
| 62 | + - **Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU):** Executes an instruction fetched from the RAM and plces the results in memory/registers |
| 63 | + - **Main Memory:** RAM |
| 64 | + - **Input/Output devices:** Devices like keyboard, mouse, monitors... |
| 65 | + |
| 66 | +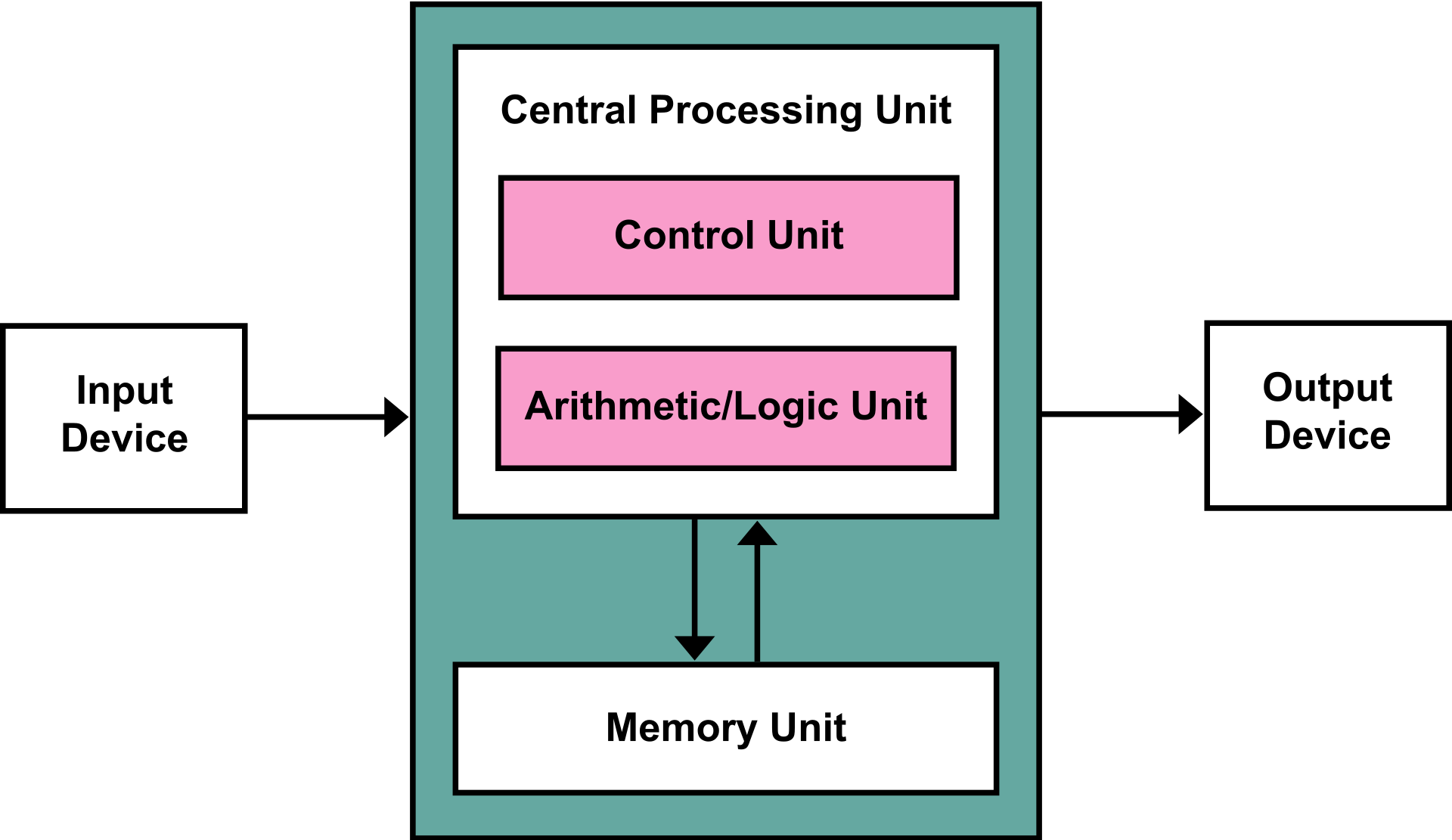 |
| 67 | + |
48 | 68 | ## Tools |
49 | 69 |
|
50 | 70 | - [Detect It Easy](https://github.com/horsicq/Detect-It-Easy): Detect file and packed types. |
|
0 commit comments